
Milk, cheese, yogurt, and dark green leafy vegetables are good sources of calcium. The human body needs adequate supplies of calcium for healthy bones. Stem cell therapy: Stem cell-derived therapies may assist in the healing of bone fractures.Ī person can reduce their risk of bone fractures through a number of remedies and lifestyle changes.Ī person’s diet can affect their risk of fractures.Bone graft: If the fracture does not heal, a surgeon will transplant a natural or synthetic bone to stimulate the broken bone.
Comminuted open fracture professional#
Comminuted open fracture skin#
Once a medical professional has aligned the fracture, they will ensure it stays in place. However, in some instances, this may require surgery. In smaller fractures, a doctor can do this by manipulating the affected area externally.

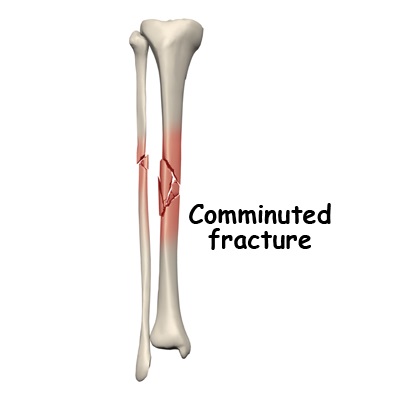
This involves lining up the ends of the broken bones. Therefore, treatment typically focuses on providing the injured bone with the best circumstances for healing, and ensuring optimal future function.įor the natural healing process to begin, a doctor will reduce the fracture. Often, they will order an X-ray, and in some cases, an MRI or CT scan, to fully assess the fracture.īone healing is a natural process that, in most cases, will occur naturally. They will then carry out a physical examination to reach a diagnosis. Transverse fracture: This is a straight break across the bone.Ī doctor will inquire about the circumstances that led to a person’s fracture.Stress fracture: Repeated stress and strain can fracture a bone.Spiral fracture: Here, at least one part of the bone twists during a break.Pathological fracture: This occurs when an underlying condition weakens the bone and causes a fracture.Oblique fracture: An oblique fracture is one that occurs opposite to a bone’s long axis.Longitudinal fracture: This is when the fracture extends along the length of the bone.Intra-articular fracture: This occurs when a fracture extends into the surface of a joint.Impacted fracture: When a bone fractures, a piece of the bone may impact another bone.Hairline fracture: This is a thin, partial fracture of the bone.Greenstick fracture: The bone partly fractures on one side but does not break completely, because the rest of the bone can bend.Fracture dislocation: This occurs when a joint dislocates, and one of the bones of the joint fractures.For example, the front portion of a vertebra in the spine may collapse due to osteoporosis. Compression, or crush, fracture: This generally occurs in the spongy bone in the spine.Comminuted fracture: An impact shatters the bone into many pieces.Avulsion fracture: A muscle or ligament pulls on the bone, fracturing it.There are a number of other fracture types, including:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
